AARP Hearing Center
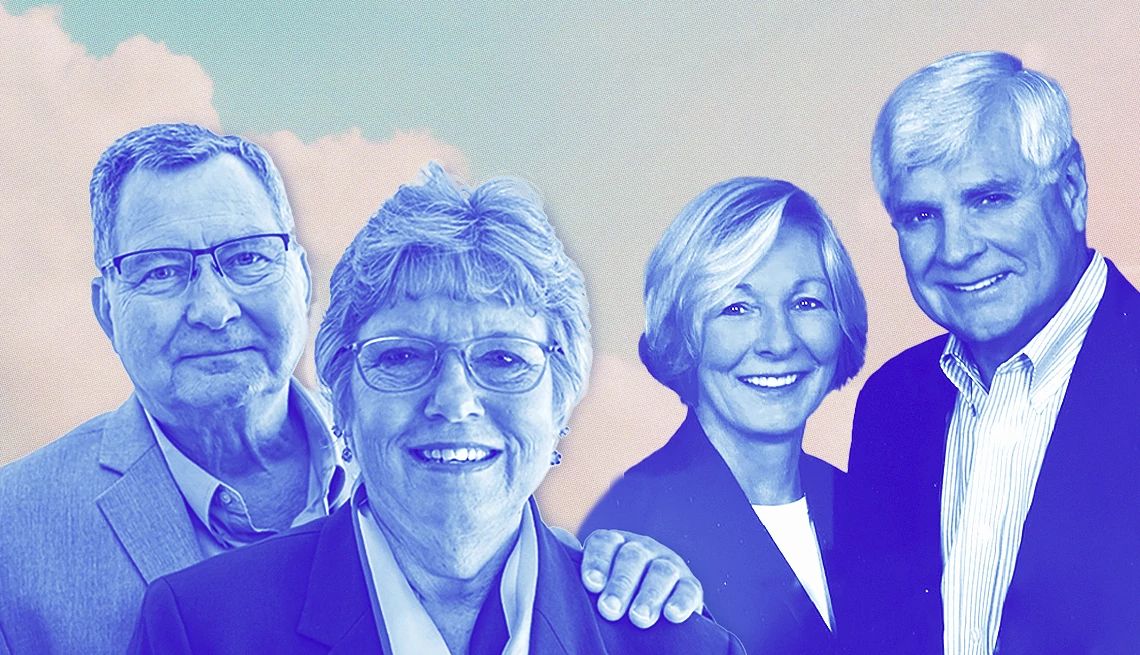


Darlene Bradley, 63, of New Palestine, Indiana, has seen dementia from both sides: first as a caregiver for her late parents, who both had Alzheimer’s disease, and now as someone living with an Alzheimer’s diagnosis since 2017.
She has some advice for anyone who cares for a loved one with dementia: Be “forgiving, not only to your loved one with the disease but forgiving of yourself, because I don’t think you would find a caregiver who could honestly say that they hadn’t been short with their loved ones or gotten frustrated.”


AARP Membership— $12 for your first year when you sign up for Automatic Renewal
Get instant access to members-only products and hundreds of discounts, a free second membership, and a subscription to AARP the Magazine.
It’s not surprising that many dementia caregivers get frustrated, stressed out or depressed. They are more likely than other caregivers for older adults to help with dressing, feeding, bathing, toileting or changing adult briefs, according to survey data from the Alzheimer’s Association.
They also face the reality that dementia, in its many forms, isn’t just about losing memory, says Helen Kales, M.D., a professor of psychiatry at UC Davis. “The day-to-day management of dementia is largely centered around behavioral and psychological symptoms,” such as agitation, hallucinations and wandering, she says. Those can be challenging for any caregiver.
Too often, caregivers face these challenges with little support, even though it’s available, says Monica Moreno, senior director of dementia care navigation at the Alzheimer’s Association.
“Unfortunately, there are far too many families that believe that they have to go through this disease alone,” she says.
Here’s what professionals and veteran caregivers say every dementia caregiver should know.
Diagnosis matters
It’s not uncommon that families notice signs of dementia but don’t seek a diagnosis, says Elizabeth Edgerly, a clinical psychologist who is senior director of care and support programs at the Alzheimer's Association. In many other cases, she says, doctors tell patients they have dementia but not what kind it is.
Alzheimer’s is the most common form of dementia, but there are others. Symptoms can vary. The common thread is that they impair memory, thinking, reasoning and behavior, according to the National Institute on Aging.
In some situations, getting an exact diagnosis might not matter, Edgerly says — for example, if someone is very near the end of life.
But more often, she says, “knowledge is power.”
She says her late mother had Lewy body dementia, which can cause sleep disturbances. After family members started struggling to awaken her, a doctor assured them that such problems are common in that disorder, Edgerly says.
Other forms include vascular dementia, which is caused by poor blood flow to the brain, and frontotemporal dementia, a rarer type that often starts with language, movement or emotional problems in midlife. Alzheimer’s disease most often starts with gradual memory loss after age 65 — though some people develop it earlier. Other diseases, such as Huntington’s, can cause dementia. Some people have “mixed dementia,” meaning more than one type.
Getting a diagnosis might start with a visit to your loved one’s primary doctor. A specialist might narrow down the diagnosis with brain scans and tests of blood and spinal fluid. If Alzheimer’s is a possibility, the tests may check for a key sign: high levels of a protein called beta-amyloid that build up in the brain.






























































More From AARP
Dementia Caregiver's Guide: Tips for Unique Challenges
The latest research on dementia, plus tips for caregivers to keep your loved ones safe
25 Great Ways to Build Healthy Habits
These tips can help create changes that positively impact your well-being for years to comeImpactful Exercises Caregivers Can Help Loved Ones Do From Bed
Small daily movements assist a person on the road to recoveryRecommended for You